Custom Rich-Text Page
The periosteum is a thin layer of connective tissue that covers the outer surface of a bone in all places except at joints (which are protected by articular cartilage). As opposed to bone itself, it has nociceptive nerve endings, making it very sensitive to manipulation. It also provides nourishment in the form of blood supply to the bone. The periosteum is connected to the bone by strong collagenous fibres called Sharpey's fibres, which extend to the outer circumferential and interstitial lamellae of bone. The periosteum consists of an outer "fibrous layer" and inner "cambium layer". The fibrous layer contains fibroblasts while the cambium layer contains progenitor cells which develop into osteoblasts that are responsible for increasing bone width. After a bone fracture the progenitor cells develop into osteoblasts and chondroblasts which are essential to the healing process.
Dextrin
re. <<wax>>
- Water. When passing a stone, upping your water intake can help speed up the process. ...
- Lemon juice. ...
- Basil juice. ...
- Apple cider vinegar. ...
- Celery juice. ...
- Pomegranate juice. ...
- Kidney bean broth. ...
- Dandelion root juice.
STRESS HORMONES
Stress induces the hypothalamic production and release of CRH, which then causes the activation of the CRH receptor (CRHR) type 1 (CRHR-1) in the anterior pituitary to stimulate ACTH release, as well as proopiomelanocortin (POMC) expression and processing.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is a hormone that stimulates the production of cortisol. Cortisol is a steroid hormone made by the adrenal glands that is important for regulating glucose, protein, and lipid metabolism, suppressing the immune system's response, and helping to maintain blood pressure.
generation of melanocyte-stimulating hormone
…from a protein known as proopiomelanocortin (POMC) and secreted primarily by the pituitary gland.
- relating to or denoting organic compounds in which carbon atoms form open chains (as in the alkanes), not aromatic rings.
Causes
Peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage) and lower extremity ischemia (lack of blood flow) due to peripheral artery disease are the primary causes of diabetic foot ulcers.
might go completely unnoticed because of numbness and lack of sensation
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is a precipitating factor in almost 90% of diabetic foot ulcers. Chronically high glucose (blood sugar) levels damage nerves, including the sensory, motor and autonomic nerves. Diabetic neuropathy also damages the immune system and impairs the body's ability to fight infection.
Sensory nerves enable people to feel pain, temperature, and other sensations. When sensory nerves of a diabetic person are damaged (sensory neuropathy), they may no longer be able to feel heat, cold, or pain in their feet.
Peripheral neuropathy also causes muscle weakness and loss of reflexes, especially at the ankle. This may change the way a person walks and lead to foot abnormalities and deformities such as bunions, hammertoes, and charcot foot. These play an important role in the pathway of diabetic foot ulcers since they contribute to abnormal pressures in the plantar area (heel and bottom) of the foot, predisposing it to ulceration.
Peripheral Artery Disease
Diabetes also damages blood vessels by causing inflammation and atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries.
deficient supply of blood to a body part (as the heart or brain) that is due to obstruction of the inflow of arterial blood (as by the narrowing of arteries by spasm or disease)
Hypoxia: A lower-than-normal concentration of oxygen in arterial blood, as opposed to anoxia, a complete lack of blood oxygen.
Symptoms of mild cerebral hypoxia include inattentiveness, poor judgment, memory loss, and a decrease in motor coordination. Brain cells are extremely sensitive to oxygen deprivation and can begin to die within five minutes after oxygen supply has been cut off.
A diabetic foot ulcer acts as a portal for systemic infections such as cellulitis, infected foot ulcers, and osteomyelitis. These are especially dangerous to patients with diabetes, whose impaired immunity increases their risk for local and systemic infection. Therefore, debridement and antibiotic therapy should be initiated as soon as possible. Blood sugar should also be monitored closely and controlled, because hyperglycemia may increase the virulence of infectious microorganisms.
- Off-loading - Relieving the pressure from the ulcerated areas by having the patient wear special foot gear, a brace, specialized castings, or using a wheelchair or crutches.
-
- Creating a moist wound environment.
- Treatment with growth factors and/or cellular therapy if the wound is not healing.
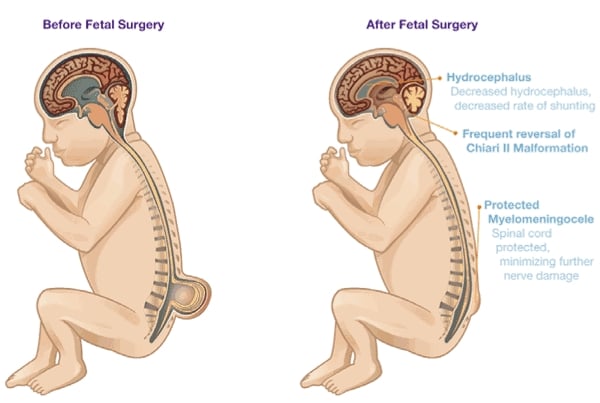
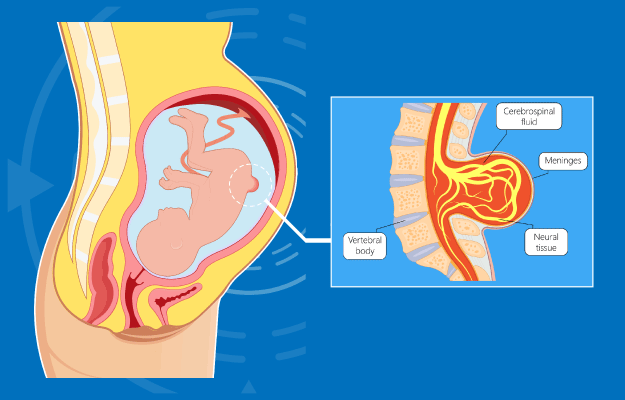
Keeping a check on these risk factors can reduce the chances of spina bifida to a large extent. Some of these risk factors are: 1. Mom-to-be is on anti-seizure medication or has diabetes. 2. Mom-to-be is older than 35 at the time of her first pregnancy. 3. Mom-to-be has a vitamin B deficiency. 4. The parents-to-be already have a child/children with a neural tube defect or Down syndrome. 5. Mom-to-be is obese. 6. Mom-to-be has high body temperature during pregnancy. Folate deficiency may cause spina bifida Folate is the natural form of vitamin B9. It’s very important for the healthy development of a baby, and a vitamin B deficiency can cause spina bifida and other neural tube defects. The synthetic form of folate, called folic acid, is found in nutritional supplements and fortified foods, and pregnant women are compulsorily recommended doses of it to take during the gestation period
Distention: The state of being distended, enlarged, swollen from internal pressure. For example, on inhalation there is distention of the lungs due to the increased air pressure within the lungs. The word "distention" comes from a Latin root "tendere," to extend. The word "tendon" comes from the same root.